Failing to connect your OBD2 scanner to your car’s ECU can be frustrating. This comprehensive guide explores common causes and provides step-by-step solutions to get your scanner working again.
Understanding OBD2 Scanner Connection Issues
OBD2 scanners are essential tools for diagnosing car problems. However, various factors can prevent them from connecting to the ECU. A successful diagnosis depends on understanding these potential issues:
- Power Supply Problems: A low car battery or a faulty OBD2 port can prevent the scanner from powering on.
- OBD2 Port Damage: Physical damage, debris, or corroded pins can obstruct the connection.
- Scanner Compatibility: Your scanner might not be compatible with your car’s make, model, or communication protocol.
- Blown Fuse: A blown fuse related to the OBD2 system can cut off power to the port.
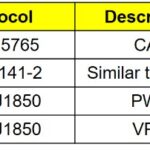
- Communication Protocol Mismatch: Using the wrong communication protocol (e.g., CAN, ISO 9141, KWP2000) can hinder connection.
- Software Problems: Outdated or corrupted scanner software can lead to connectivity issues.
Common Causes and Solutions
Power Supply
Ensure your car battery is fully charged. Use a multimeter to verify that the OBD2 port receives around 12 volts.
OBD2 Port Inspection
Carefully examine the OBD2 port for any visible damage, loose wires, bent pins, or debris. Clean the port with compressed air.
Scanner Compatibility Check
Confirm your scanner’s compatibility with your car’s make and model. Consult the scanner’s manual or the manufacturer’s website.
Fuse Examination
Locate the fuse box (usually under the dashboard or in the engine compartment) and check the fuse related to the OBD2 system. Replace any blown fuses with the correct amperage.
Communication Protocol Selection
Determine your car’s communication protocol (refer to your car’s manual) and ensure your scanner is set to the same protocol. Many modern scanners automatically detect the correct protocol.
Software Update
Update your scanner’s software to the latest version. This can often resolve compatibility issues and improve performance.
Troubleshooting Steps with an OBD2 Scanner
Using a reliable diagnostic tool like the Foxwell NT809 can simplify troubleshooting.
Power Verification
Turn the ignition to the accessory position. Use a multimeter or the scanner’s voltage check feature to confirm power at the OBD2 port.
Port Examination
Visually inspect the OBD2 port and clean it with compressed air.
Compatibility Confirmation
Verify scanner compatibility with your car.
Fuse Check
Locate and check the OBD2 system fuse. Replace if necessary.
Protocol Setting
Set the scanner to the correct communication protocol.
Software Update Execution
Connect the scanner to a computer and update its software.
Advanced Troubleshooting Tips
- Connection Verification: Double-check the connection between the scanner and the port.
- Wiring Harness Inspection: Examine the wiring leading to the OBD2 port for damage.
- Port Cleaning: Clean the OBD2 port with electrical contact cleaner.
- Testing on Another Car: Try connecting the scanner to a different car to rule out scanner issues.
- Backup Scanner Utilization: Use a different scanner to isolate the problem.
- Hidden Fuse Check: Consult your car’s service manual for hidden fuses.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting an OBD2 scanner that won’t connect to the ECU requires a systematic approach. By following this guide, you can identify the root cause and resolve the issue. If problems persist, consult a qualified mechanic. Regular maintenance and keeping your scanner’s software updated can prevent future connection problems.