OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics, is a system in your vehicle that allows you to access real-time data and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). This is done using an OBD2 scanner connected to the OBD2 port, usually located near the steering wheel. A key component of understanding and utilizing OBD2 is the Parameter ID (PID). This article will delve into what an OBD2 PID number is, provide examples, and explain how it works within the broader OBD2 framework.
Understanding OBD2 PIDs
OBD2 PIDs are hexadecimal codes that represent specific parameters or data points that can be requested from a vehicle’s ECU (Engine Control Unit). Each PID corresponds to a specific piece of information, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, or fuel level. When an OBD2 scanner requests a specific PID, the vehicle’s ECU responds with the corresponding data.
Example of a OBD2 PID Number: Vehicle Speed
One of the most common examples of a OBD2 PID number is 0x0D, which represents vehicle speed. When a scanner requests this PID, the vehicle responds with a single byte of data representing the speed in kilometers per hour (km/h). For instance, a response of 0x32 would indicate a speed of 50 km/h.
OBD2 Modes and PIDs
OBD2 PIDs are organized into different modes, each representing a different diagnostic service. Mode 0x01, for instance, focuses on current powertrain diagnostic data and includes a wide range of PIDs related to engine performance, emissions, and other vital parameters. A crucial PID within Mode 0x01 is 0x00, which indicates the supported PIDs for that specific vehicle.
OBD2 PID Lookup and Decoding
While knowing an Example Of A Obd2 Pid Number is helpful, understanding how to decode the data is essential. Resources like SAE J1979 and ISO 15031-5 provide detailed information on PID scaling and decoding. Online OBD2 PID lookup tools offer a convenient way to find specific PIDs and their corresponding decoding formulas. This allows you to translate the raw data received from the vehicle into meaningful values.
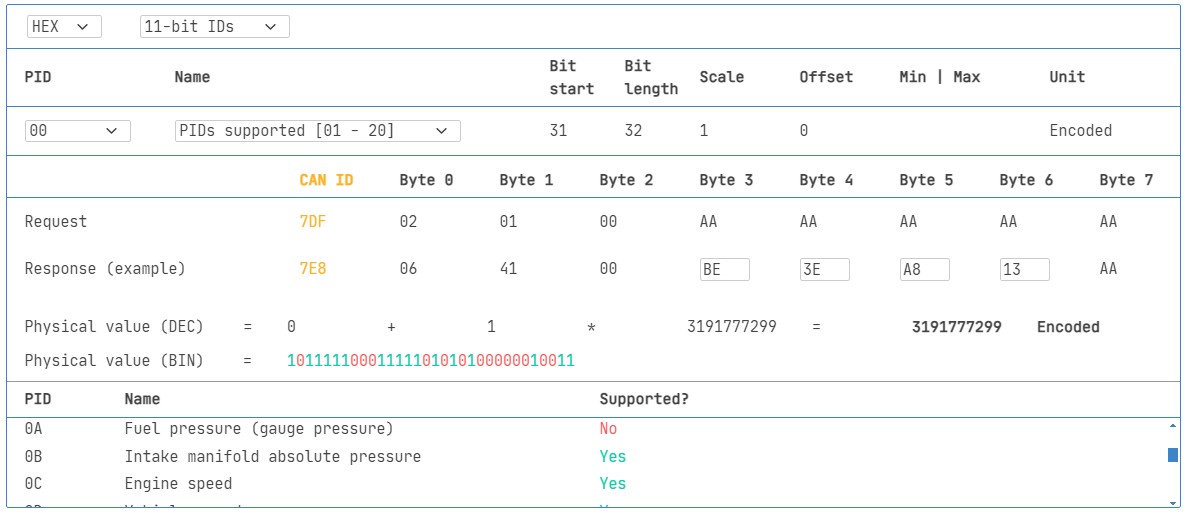 Review supported PIDs via OBD2 lookup tool
Review supported PIDs via OBD2 lookup tool
Practical Application of OBD2 PIDs
Understanding and utilizing OBD2 PIDs is crucial for various applications, including:
- Diagnostics: Mechanics use OBD2 scanners to retrieve DTCs and real-time data using PIDs to diagnose vehicle issues efficiently.
- Performance Tuning: Enthusiasts and professionals use OBD2 data to monitor and optimize vehicle performance by analyzing PIDs related to engine parameters.
- Fleet Management: Businesses track vehicle data, including fuel consumption, speed, and location, using OBD2 PIDs for efficient fleet management.
OBD2 and CAN Bus
Most modern vehicles utilize the CAN (Controller Area Network) bus for communication, and OBD2 leverages this protocol for data transmission. ISO 15765-4 defines how OBD2 operates over CAN, specifying details such as CAN IDs (0x7DF for requests, 0x7E8 for responses) and data formatting. This standardized framework ensures compatibility across various vehicle makes and models.
Conclusion
Understanding examples of OBD2 PID numbers is fundamental to effectively using the OBD2 system. By requesting specific PIDs, users can access a wealth of information about a vehicle’s performance, emissions, and overall health. Combining this knowledge with decoding resources and tools empowers both professionals and enthusiasts to diagnose issues, optimize performance, and gain valuable insights into their vehicles. While this guide focused on common examples, remember that there are numerous other PIDs available, each providing unique data points for specific diagnostic and monitoring purposes.