A failing alternator can lead to a variety of electrical problems in your vehicle, from dimming headlights to a dead battery. An Obd2 Alternator Test can help pinpoint the issue. This article will guide you through using an OBD2 scanner, like the Foxwell NT1009, to check your alternator’s health. We’ll also discuss alternative testing methods.
How an Alternator Works and Signs of Failure
The alternator is a crucial part of your car’s electrical system. It generates electricity to power everything from the headlights to the radio and, most importantly, recharges the battery. A malfunctioning alternator can leave you stranded. Common signs of a failing alternator include:
- Dimming headlights
- Slow engine crank
- Dead battery
- Warning lights on the dashboard
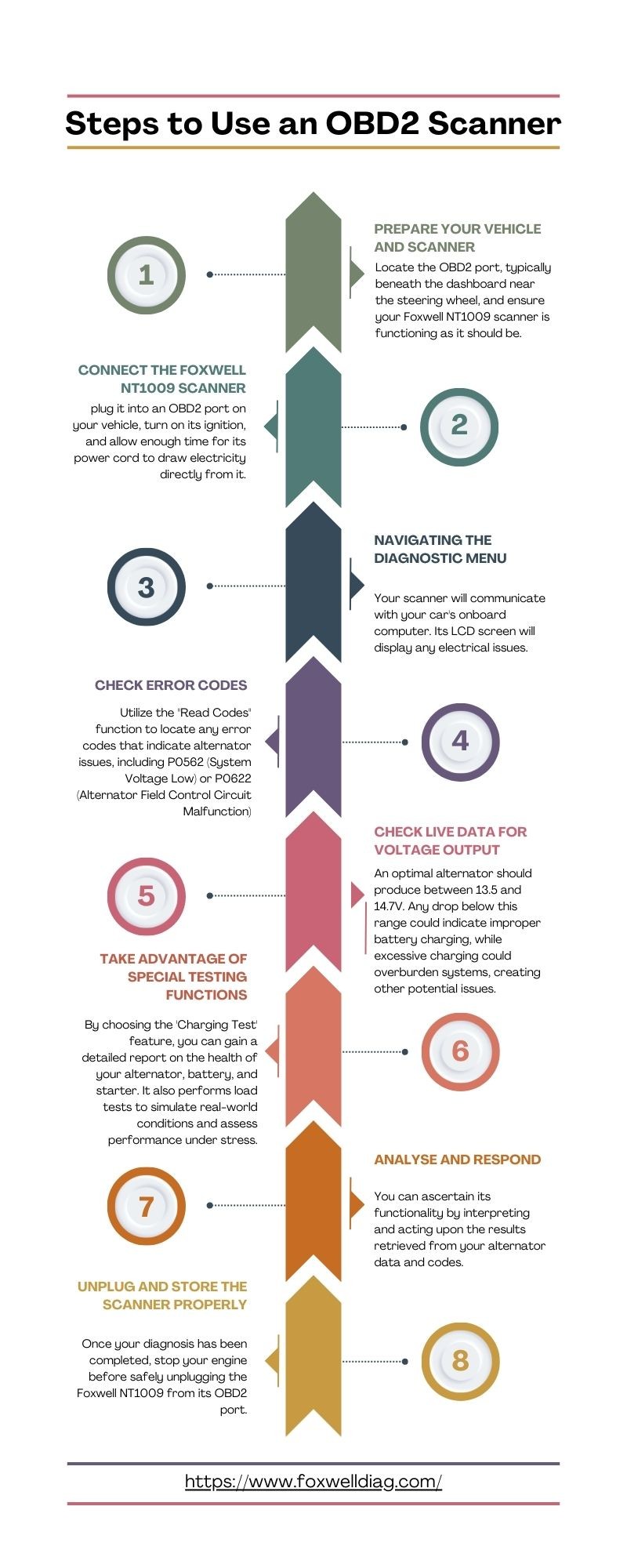
Using an OBD2 Scanner for Alternator Diagnostics
While an OBD2 scanner won’t directly tell you “bad alternator,” it can provide valuable clues. It reads trouble codes stored in your car’s computer, which can point to alternator-related problems. Here’s how to perform an OBD2 alternator test:
Connecting and Setting Up the Scanner
- Turn off all unnecessary electrical accessories.
- Locate the OBD2 port (usually under the dashboard).
- Connect the OBD2 scanner (e.g., Foxwell NT1009).
- Turn the ignition to the “on” position (don’t start the engine).
Reading Trouble Codes
- Navigate to the “Diagnostic” menu on the scanner.
- Select your vehicle’s make and model.
- Choose “Read Codes.”
- Look for codes related to low voltage (P0562) or alternator field control circuit issues (P0622).
Monitoring Live Data
- Start the engine.
- Select “Live Data” on the scanner.
- Observe the voltage reading. A healthy alternator should output between 13.5 and 14.7 volts. Low voltage indicates a potential problem.
- Turn on electrical accessories (headlights, A/C) to see if the voltage drops significantly under load.
Running Specialized Tests
Some scanners offer specific alternator tests. The Foxwell NT1009, for example, has a “Charging Test” function that provides a detailed report on the alternator, battery, and starter.
Alternative Alternator Testing Methods
If your OBD2 alternator test is inconclusive, you can try these methods:
Multimeter Test
Connect a multimeter to the battery terminals while the engine is running. A reading between 13.5 and 14.7 volts indicates a healthy alternator.
Load Test
A load test simulates real-world conditions by placing a heavy electrical load on the alternator. This test requires specialized equipment and is often performed by a mechanic.
Conclusion: OBD2 Scanners as a Diagnostic Tool
An OBD2 alternator test can be a valuable first step in diagnosing charging system problems. While it might not definitively diagnose a bad alternator, it provides crucial information. Combining an OBD2 scan with other testing methods can help you confidently determine if your alternator needs repair or replacement. Regular OBD2 scans can help prevent unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.