The complexity of modern vehicles demands sophisticated diagnostic tools. These tools rely heavily on Obd2 Map Reading to gather crucial data from various sensors, including the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This article delves into the importance of the MAP sensor, symptoms of failure, and how OBD2 scanners aid in diagnosis.
The MAP sensor is a critical component in a vehicle’s engine management system. It measures the pressure inside the intake manifold and relays this information to the Engine Control Unit (ECU). This data is essential for optimizing engine performance, controlling turbocharger/supercharger boost, and enabling on-board diagnostics.
The Crucial Role of the MAP Sensor in Engine Management
The MAP sensor plays a vital role in ensuring optimal engine performance and efficiency. It contributes to several key functions:
-
Optimizing Engine Performance: The MAP sensor provides real-time data to the ECU, allowing it to adjust the air/fuel mixture and ignition timing for optimal power and fuel efficiency. Accurate map reading ensures smooth running and prevents issues like rough idling or stalling.
-
Controlling Turbo/Supercharger Boost: In turbocharged or supercharged engines, the MAP sensor monitors boost pressure. This allows the ECU to regulate boost levels, preventing overboost and potential engine damage. Precise obd2 map reading is crucial for maintaining performance and longevity in these engines.
-
On-Board Diagnostics: The MAP sensor’s voltage is constantly monitored by the ECU. Deviations from expected values trigger Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), which can be read by an OBD2 scanner. This facilitates quick and accurate diagnosis of potential issues within the engine management system.
Recognizing Symptoms of a Faulty MAP Sensor
A failing MAP sensor often manifests through various performance issues, often accompanied by an illuminated Check Engine Light (CEL). Common symptoms include:
-
Deteriorated Engine Performance: A faulty MAP sensor can cause rough idling, stalling, hesitation, reduced power, and poor acceleration. These issues stem from inaccurate pressure readings, leading to incorrect fuel delivery and inefficient combustion.
-
Decreased Fuel Economy: Inaccurate map reading can disrupt the air/fuel ratio, resulting in incomplete combustion and wasted fuel. This leads to a noticeable drop in fuel mileage, requiring more frequent refueling.
Utilizing OBD2 Scanners for MAP Sensor Diagnosis
An OBD2 scanner is indispensable for accurately diagnosing MAP sensor problems. These scanners provide detailed insights into sensor data, including voltage readings and DTCs.
Connecting the scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port allows access to real-time data and enables specific tests to pinpoint the issue. Common DTCs related to MAP sensor malfunctions include:
| DTC Code | Description |
|---|---|
| P0105 | MAP Sensor Circuit Malfunction |
| P0106 | MAP Sensor Performance |
| P0107 | MAP Sensor Circuit Low Input |
| P0108 | MAP Sensor Circuit High Input |
| P0109 | MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent |
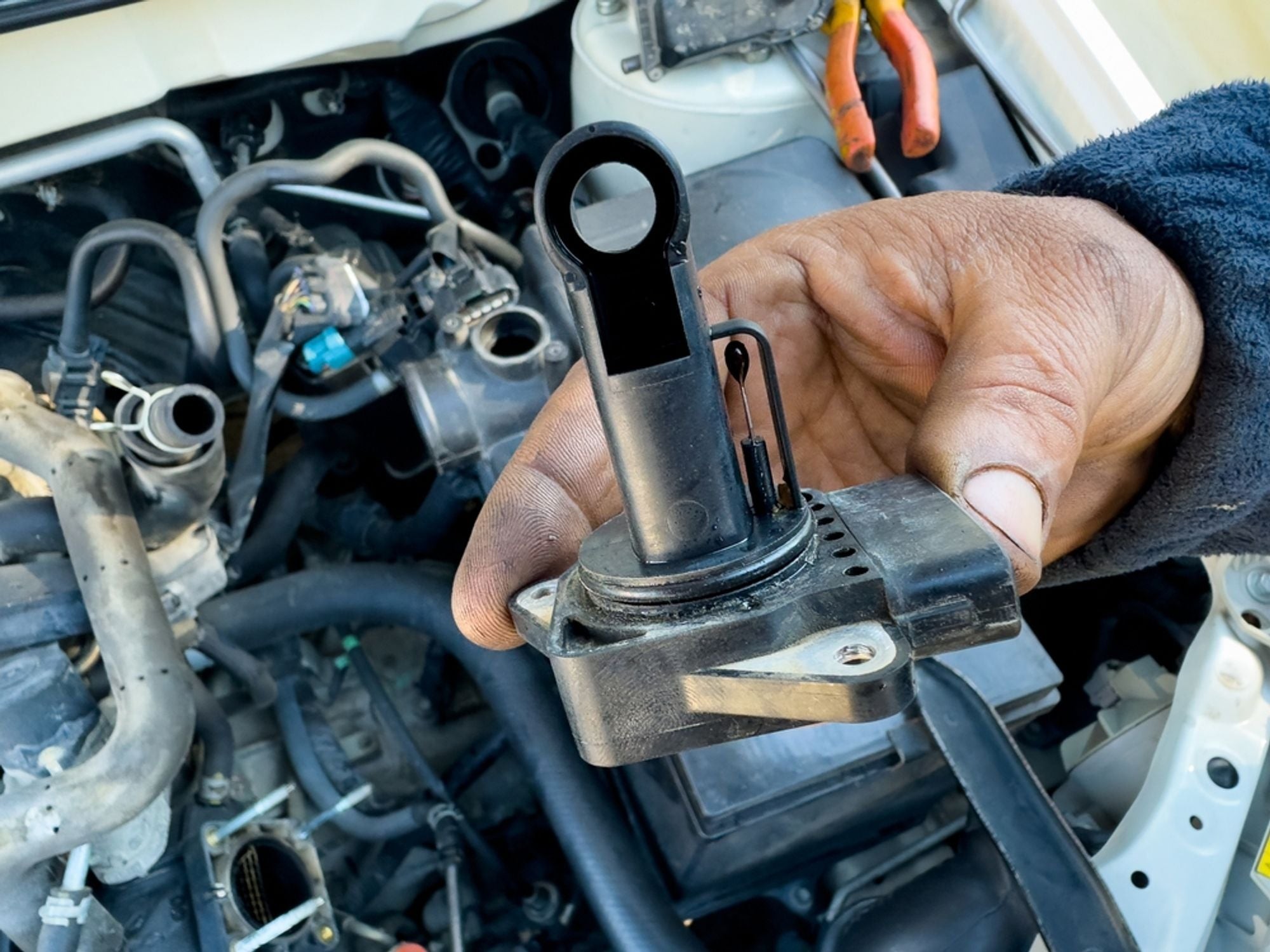
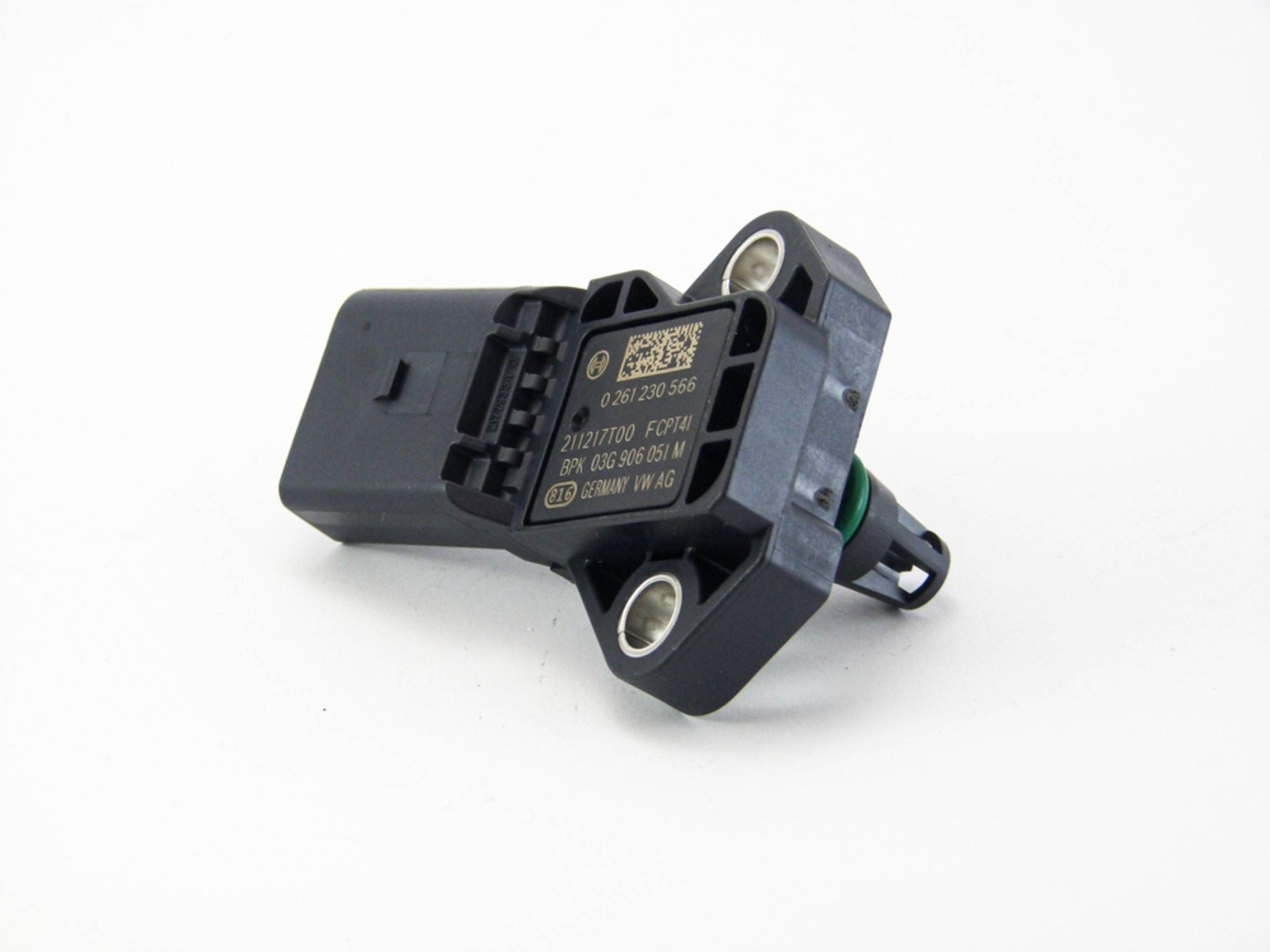



These codes provide valuable clues for identifying the specific problem with the MAP sensor, enabling targeted repairs.
Understanding the Causes of MAP Sensor Failure
Several factors can contribute to MAP sensor failure:
-
Contamination: Oil, dirt, or debris can clog the sensor, affecting its accuracy.
-
Electrical Problems: Damaged wiring, loose connections, or blown fuses can disrupt the sensor’s operation.
-
Physical Damage: Excessive heat, vibration, or impact can damage the sensor itself.
Regular maintenance and prompt diagnosis using OBD2 map reading are crucial for preventing and addressing MAP sensor issues, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.